Always a leader. Always dependable.
Grifols has provided more than 45 years of consistent supply and product support.
HyperHEP B is an immunoglobulin that provides rapid immune coverage.1 Vaccines can provide lifelong protection but take weeks to build efficacy, however, HyperHEP B provides immediate protection that allows the vaccine the time needed to establish active immunity in high-risk situations.1-3
HyperHEP B contains high titers of antibodies, equivalent to or exceeding the potency of anti-HBs in a US reference hepatitis B immune globulin standard (established by the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, FDA), and provides rapid immune protection for postexposure prophylaxis (PEP).1,2
The vaccine alone is not enough: immune globulins like HyperHEP B, when used in combination with a vaccine, can prevent infection by hepatitis B. The administration of the recommended dose of this immune globulin generally results in a detectable level of circulating anti-HBs, which persists for approximately 2 months or longer.
Grifols has provided more than 45 years of consistent supply and product support.

HyperHEP B is produced using a sophisticated caprylate/chromatography purification process that employs the highest quality and safety standards.
Main steps of the manufacturing process:
The capacity of the HyperHEP B manufacturing process to remove and/or inactivate viruses has been demonstrated by laboratory spiking studies on a scaled-down process model using a wide range of viruses with diverse physicochemical properties. This process provides the final product with a high margin of safety from the potential risk of transmission of infectious viruses.
The caprylate/chromatography manufacturing process was also investigated for its capacity to decrease the infectivity of an experimental agent of transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE), considered as a model for the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agents. These studies provide reasonable assurance that low levels of vCJD/CJD agent infectivity, if present in the starting material, would be removed by the caprylate/chromatography manufacturing process.

HyperHEP B is made from human blood and may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, eg, viruses, the vCJD agent, and, theoretically, the CJD agent.
Grifols' manufacturing process has a comprehensive computer system called PediGri® that ensures full traceability from every donation
Exposure to blood containing HBV
0.06 mL/kg IM as soon as possible after exposure and within 24 hours
Infants born to mothers who carry HBV
0.5 mL IM after physiologic stabilization and preferably within 12 hours of birth
Sexual contact with persons who carry HBV
0.06 mL/kg IM within 14 days of last sexual contact with infected person
All other contacts
See complete Prescribing Information
| Indication | Dosage |
|---|---|
|
Exposure to blood containing HBV |
0.06 mL/kg IM as soon as possible after exposure and within 24 hours |
|
Infants born to mothers who carry HBV |
0.5 mL IM after physiologic stabilization and preferably within 12 hours of birth |
|
Sexual contact with persons who carry HBV |
0.06 mL/kg IM within 14 days of last sexual contact with infected person |
|
All other contacts |
See complete Prescribing Information |
Product CPT Code*
90371
Hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG), human for intramuscular use (1 mL)
Administration Procedures CPT Code*
96372
Therapeutic, prophylactic, or diagnostic injection (specify substance or drug); intramuscular
ICD-10-CM†
B19.1
Unspecified viral hepatitis B
B19.10
Unspecified viral hepatitis B without hepatic coma
B19.11
Unspecified viral hepatitis B with hepatic coma
B18.1
Chronic viral hepatitis B without delta-agent
B18.0
Chronic viral hepatitis B with delta-agent
B18.9
Chronic viral hepatitis, unspecified
B18.8
Other chronic viral hepatitis
B17.0
Acute delta-(super) infection of hepatitis B carrier
B16.0
Acute hepatitis B with delta-agent with hepatic coma
B16.9
Acute hepatitis B without delta-agent and without hepatic coma
B16.1
Acute hepatitis B with delta-agent without hepatic coma
B16.2
Acute hepatitis B without delta-agent with hepatic coma
Z20.5
Contact with and (suspected) exposure to viral hepatitis
P39.9
Infection specific to the perinatal period, unspecified
Z20.2
Contact with and (suspected) exposure to infections with a predominantly sexual mode of transmission
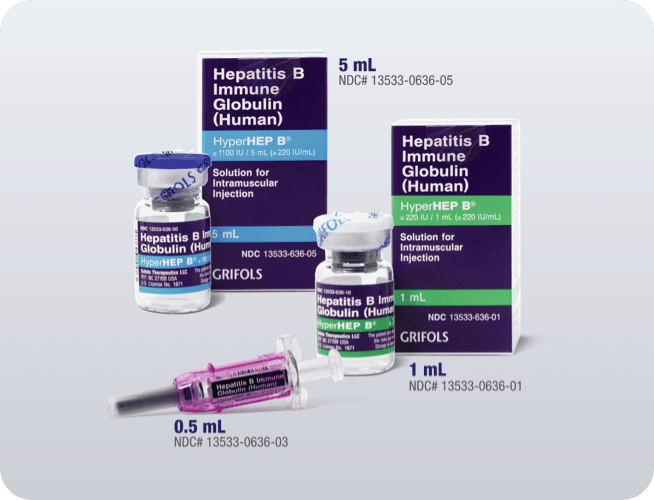
Product NDC‡
13533-0636-03
0.5-mL syringe
13533-0636-01
1-mL vial
13533-0636-05
5-mL vial
| Coding System | Coding for HyperHEP B | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Product CPT Code* |
90371 |
Hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG), human for intramuscular use (1 mL) |
|
Administration Procedures CPT Code* |
96372 |
Therapeutic, prophylactic, or diagnostic injection (specify substance or drug); intramuscular |
|
ICD-10-CM† |
B19.1 |
Unspecified viral hepatitis B |
|
B19.10 |
Unspecified viral hepatitis B without hepatic coma |
|
|
B19.11 |
Unspecified viral hepatitis B with hepatic coma |
|
|
B18.1 |
Chronic viral hepatitis B without delta-agent |
|
|
B18.0 |
Chronic viral hepatitis B with delta-agent |
|
|
B18.9 |
Chronic viral hepatitis, unspecified |
|
|
B18.8 |
Other chronic viral hepatitis |
|
|
B17.0 |
Acute delta-(super) infection of hepatitis B carrier |
|
|
B16.0 |
Acute hepatitis B with delta-agent with hepatic coma |
|
|
B16.9 |
Acute hepatitis B without delta-agent and without hepatic coma |
|
|
B16.1 |
Acute hepatitis B with delta-agent without hepatic coma |
|
|
B16.2 |
Acute hepatitis B without delta-agent with hepatic coma |
|
|
Z20.5 |
Contact with and (suspected) exposure to viral hepatitis |
|
|
P39.9 |
Infection specific to the perinatal period, unspecified |
|
|
Z20.2 |
Contact with and (suspected) exposure to infections with a predominantly sexual mode of transmission |
|
|
Product NDC‡ |
13533-0636-03 |
0.5-mL syringe |
|
13533-0636-01 |
1-mL vial |
|
|
13533-0636-05 |
5-mL vial |
Important Safety Information for HyperHEP B® (hepatitis B immune globulin [human])
HyperHEP B® (hepatitis B immune globulin [human]) is indicated for postexposure prophylaxis in the following situations: acute exposure to blood containing HBsAg, perinatal exposure of infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers, sexual exposure to an HBsAg-positive person, and household exposure to persons with acute HBV infection.
HyperHEP B should be given with caution to patients with a history of prior systemic allergic reactions following the administration of human immunoglobulin preparations. Epinephrine should be available.
In patients who have severe thrombocytopenia or any coagulation disorder that would contraindicate intramuscular injections, hepatitis B immune globulin (human) should be given only if the expected benefits outweigh the risks.
Local pain and tenderness at the injection site, urticaria, and angioedema may occur; anaphylactic reactions, although rare, have been reported following the injection of human immunoglobulin preparations. Administration of live virus vaccines (eg, MMR) should be deferred for approximately 3 months after hepatitis B immune globulin (human) administration.
HyperHEP B is made from human plasma. Products made from human plasma may contain infectious agents, such as viruses, and, theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent that can cause disease. There is also the possibility that unknown infectious agents may be present in such products.
Please see full Prescribing Information for HyperHEP B.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
References